Artificial Intelligence (AI) has evolved significantly over the past few decades, transitioning from rule-based systems to more sophisticated models capable of learning and adapting. A notable advancement in this evolution is the emergence of agentic AI, a paradigm that introduces a new level of autonomy and decision-making capabilities in AI systems.
Understanding Agentic AI
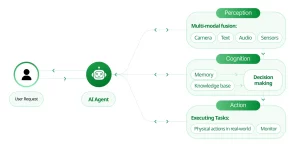
Agentic AI refers to AI systems designed to act autonomously, making decisions and performing tasks without continuous human intervention. Unlike traditional AI models that rely on predefined rules or direct human input, agentic AI systems can analyze complex data, set goals, and execute multi-step plans to achieve those goals. This autonomy is achieved through advanced techniques such as reinforcement learning, natural language processing, and large language models (LLMs).
Key Characteristics of Agentic AI
- Autonomy: The ability to operate independently, making decisions without human oversight.
- Adaptability: The capacity to learn from interactions and adjust actions based on new information.
- Goal-Oriented Behavior: Setting and pursuing objectives over extended periods.
- Complex Problem Solving: Handling multi-step tasks that require reasoning and planning.
Technological Foundations
The development of agentic AI is underpinned by several technological advancements:
- Reinforcement Learning: A type of machine learning where agents learn to make decisions by receiving rewards or penalties for their actions, enabling them to optimize their behavior over time.
- Large Language Models (LLMs): These models, such as OpenAI’s GPT series, process and generate human-like text, allowing AI systems to understand and interact using natural language.
- Cloud Computing: Provides the computational power necessary for training and deploying complex AI models at scale.
- Integration with Enterprise Systems: Agentic AI can access and process data from various business applications, enhancing its decision-making capabilities.
Applications Across Industries
Agentic AI is being implemented across various sectors to enhance efficiency and innovation:
- Healthcare: AI systems assist in diagnosing diseases, managing patient care, and personalizing treatment plans.
- Finance: In financial services, agentic AI enables high-frequency trading, fraud detection, and personalized banking experiences.
- Customer Service: AI-powered chatbots handle customer inquiries, process returns, and manage inventories autonomously.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance and supply chain optimization are achieved through AI agents analyzing real-time data from industrial equipment.
Ethical and Governance Considerations
The autonomy of agentic AI raises several ethical and governance challenges:
- Accountability: Determining responsibility when AI systems make decisions that lead to unintended consequences.
- Transparency: Ensuring that AI decision-making processes are understandable and explainable to humans.
- Bias and Fairness: Addressing potential biases in AI systems that could lead to discriminatory outcomes.
- Regulation: Developing frameworks to govern the deployment and use of agentic AI, particularly in high-risk areas like healthcare and finance.
The Future of Agentic AI
The trajectory of agentic AI suggests a future where these systems become integral to daily life and business operations. As AI continues to evolve, the focus is shifting towards creating systems that not only perform tasks but also understand context, adapt to changing environments, and collaborate with humans to solve complex problems.
In conclusion, agentic AI represents a significant leap in artificial intelligence, offering the potential to revolutionize industries and improve quality of life. However, its development and deployment must be approached with careful consideration of ethical principles and governance to ensure that these powerful tools are used responsibly and for the benefit of society.